Development Environments
Programs, languages and compilers
First steps with Python
1. Python programming language
Python is an interpreted language that is really easy to learn (it is usually chosen in many educational institutions to teach programming). Resulting code is usually much more compact and understandable that the same code in other traditional languages, for the same task. We can also develop several types of applications with this language, such as system scripts, video games (with libraries like PyGame) or server side web applications (with frameworks like Django). It is also very appreciated in some other tasks like hacking and deep learning.
2. Installing Python
Let’s try with an interpreted language such as Python. In order to install it under Windows or Mac OSX, we need to go to its official download page.
Python interpreter is usually a command called python or python3, depending on the version and operating system that we are using. Nowadays, Python 2 is no longer maintained, so we will use Python 3. For instance, in Windows Python 3 interpreter is launched through python command, whereas in Linux we use python3 command instead.
When you install Python in Windows, make sure you check the option to add Python automatically to your PATH variable. You can also change the default installation folder:
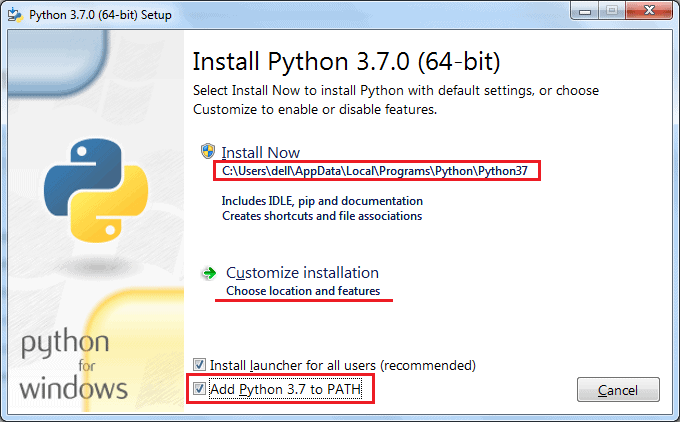
Regarding Linux, we can firstly check which version of Python we have currently installed with this command:
python3 --version
We can easily update or install from scratch Python (version 3) with these command:
sudo apt-get install python3
Exercise 1:
Create a source file called
test.pywith this source code in Python programming language:
print("Hello")
Save the changes and try to run it with one of these commands (depending on the name of your Python interpreter in your system):
python test.py
python3 test.py